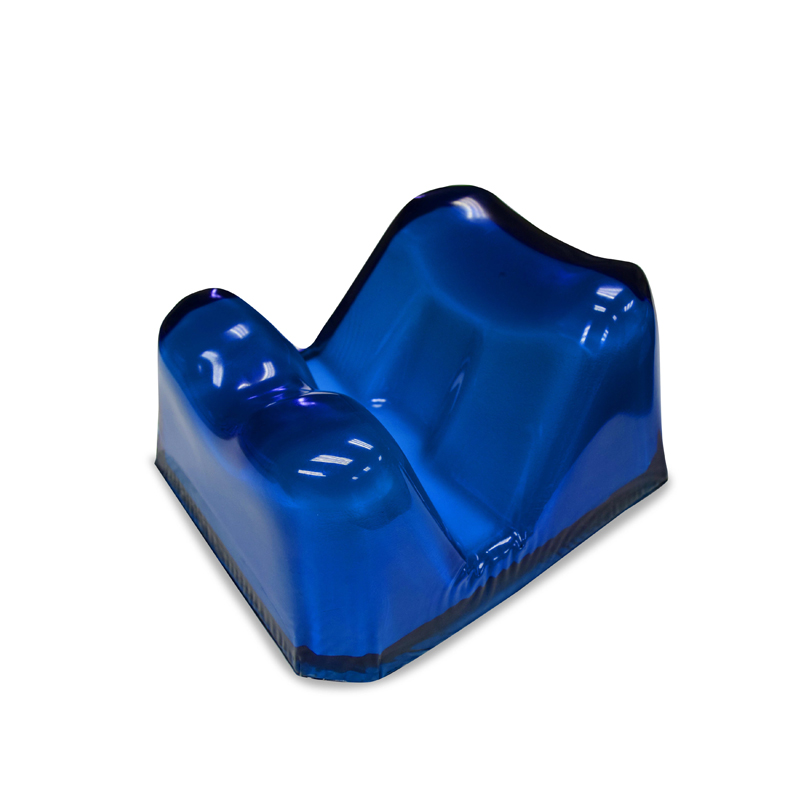
Prone head positioner ORP-PH (Prone Facial Positioner)
Prone head positioner ORP-PH
Model: ORP-PH
Function
1. To protect and support head and face in prone position
2. To facilitate general anesthesia and to maintain respiratory passageway
Dimension
28.5 x 24.5 x 14cm
Weight
3.3kg
Product parameters
Product Name: Positioner
Material: PU Gel
Definition: It is a medical device which is used in an operating room to protect patient from pressure sores during surgery.
Model: Different positioners are used for different surgical positions
Color: Yellow, blue, green. Other colors and sizes can be customized
Product characteristics: Gel is a kind of high molecular material, with good softness, support, shock absorption and compression resistance, good compatibility with human tissues, X-ray transmission, insulation, non-conductive, easy to clean, convenient to disinfect, and does not support bacterial growth.
Function: Avoid pressure ulcer caused by long operation time
Product characteristics
1. The insulation is non-conductive, easy to clean and disinfect. It does not support bacterial growth and has good temperature resistance. The resistance temperature ranges from -10 ℃ to +50 ℃
2. It provides patients with good, comfortable and stable body position fixation. It maximizes the exposure of the surgical field, reduce the operation time, maximize the dispersion of pressure, and reduce the occurrence of pressure ulcer and nerve damage.
Cautions
1. Do not wash the product. If the surface is dirty, wipe the surface with a wet towel. It can also be cleaned with neutral cleaning spray for better effect.
2. After using the product, please clean the surface of the positioners on time to remove dirt, sweat, urine, etc. The fabric can be stored in a dry place after drying in a cool place. After storage, do not put heavy objects on top of the product.
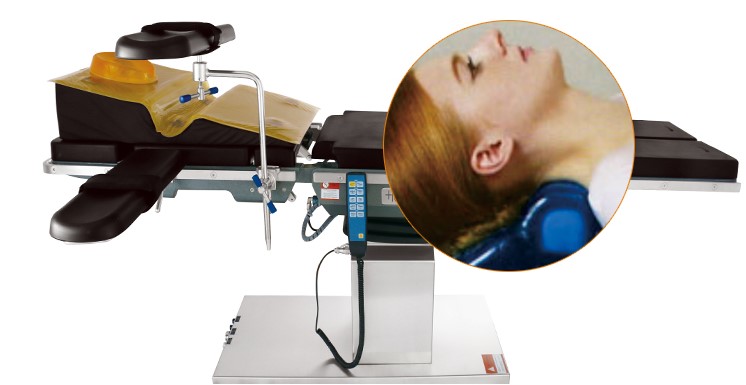
The design of prone head positioner facilitate general anesthesia and maintain respiratory passageway.
General anaesthesia is a state of controlled unconsciousness. During a general anaesthetic, medicines are used to send you to sleep, so you are unaware of surgery and do not move or feel pain while it is carried out. General anaesthesia is used for surgical procedures where it is safer or more comfortable for you to be unconscious. It is usually used for long operations or those that would otherwise be very painful.
Before and during operation
Just before having surgery, patient usually be taken to a room where anaesthetist will give the patient the general anaesthetic.
It will either be given as a:
● Liquid that is injected into patient’s veins through a cannula (a thin, plastic tube that feeds into a vein, usually on the back of your hand)
● Gas that you breathe in through a mask
The anaesthetic should take effect very quickly. The patient starts feeling lightheaded, before becoming unconscious within a minute or so.
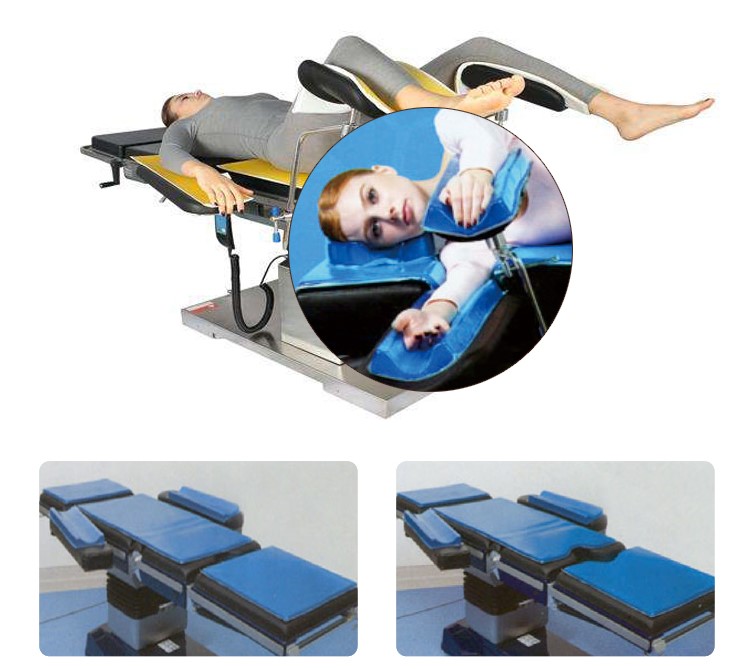
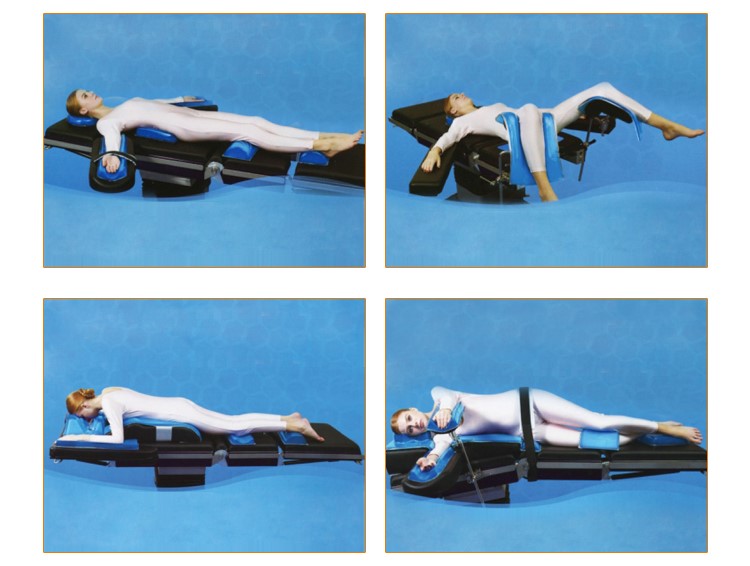
Positioning the patient:
● Anesthetize patient in the supine position and then log-roll into the prone position.
The anesthesia care provider controls the patient’s head and neck as the patient is turned.
● Pad all bony prominences and areas where the patient’s skin comes in direct contact with lines during the procedure using gel pads or jute padding.
● Arms:
o Place arms on an adequately padded arm board extended no more than 90 degrees from the patient’s body, with the arms slightly flexed and palms facing downward. Never position the arms above the patient’s head. (Rationale: prevents brachial plexus injury.)
o If position arms at patient’s sides place palms facing the body (thighs).
● Breasts, genitalia:
o Use bolsters from the clavicle to the iliac crest. (Rationale: allows for adequate chest expansion and decreases pressure to the patient’s abdomen.)
o Place bolster/pillows under hips to elevate buttock as per surgeon preference.
o Position breasts and genitalia in such a way that they are free from pressure and torsion injury during the intraoperative phase.
● Knees – use gel positioner underneath as required.
● Feet are supported so the toes hang freely.
● Place safety positioning strap across the posterior upper thigh 2 inches above the knees.
● For the obese patient, allow abdominal wall to hang freely. (Rationale: decreases diaphragm impedance and allows chest wall movement.)








